45 label an atp molecule
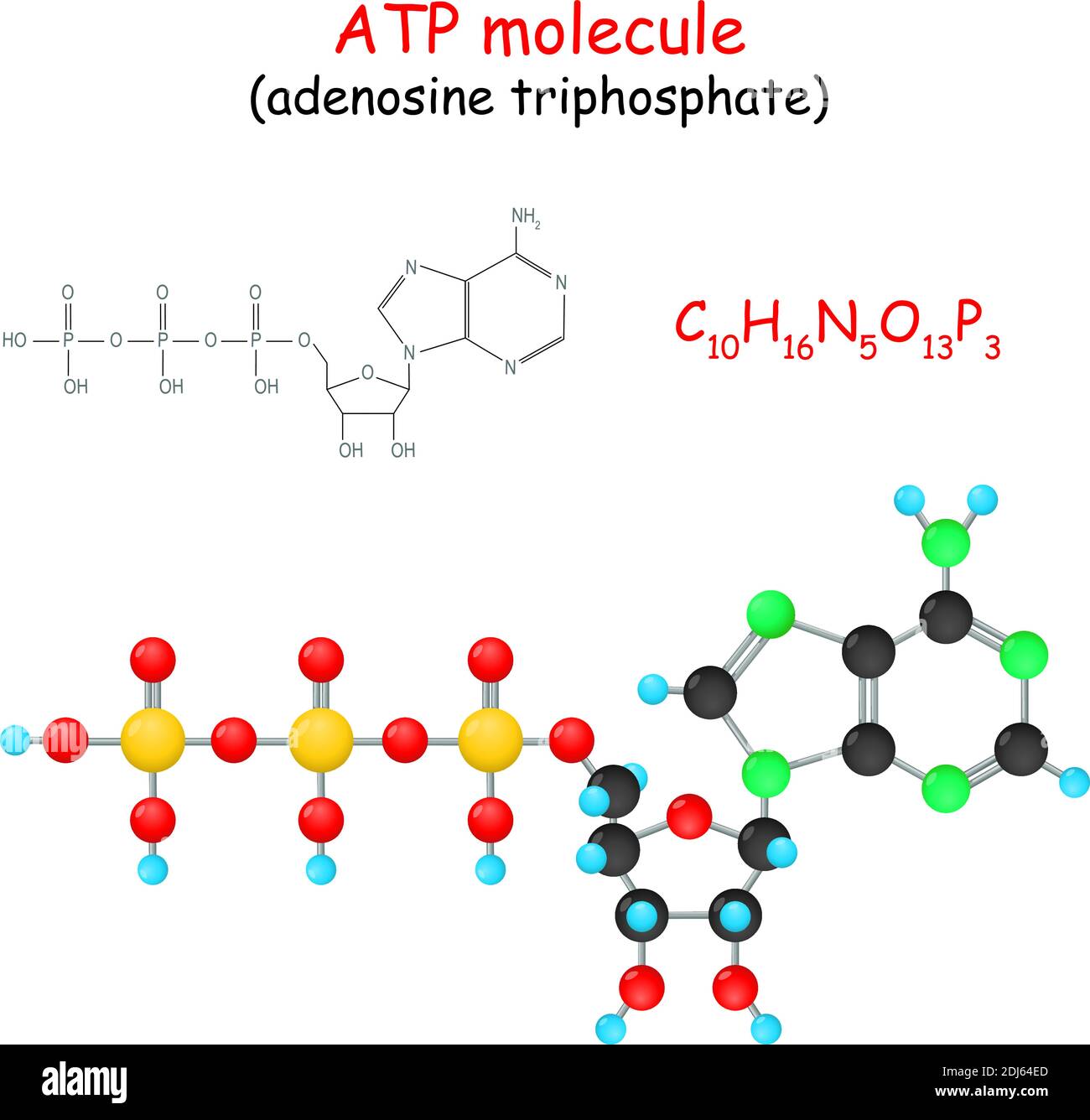
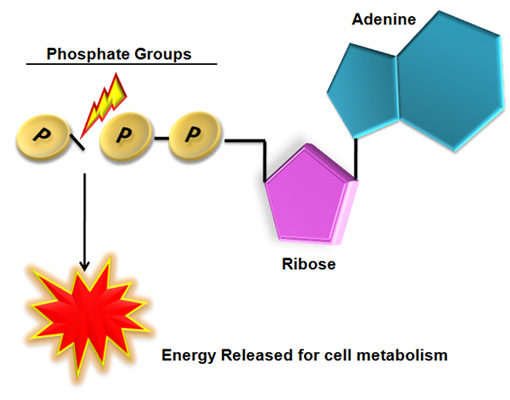
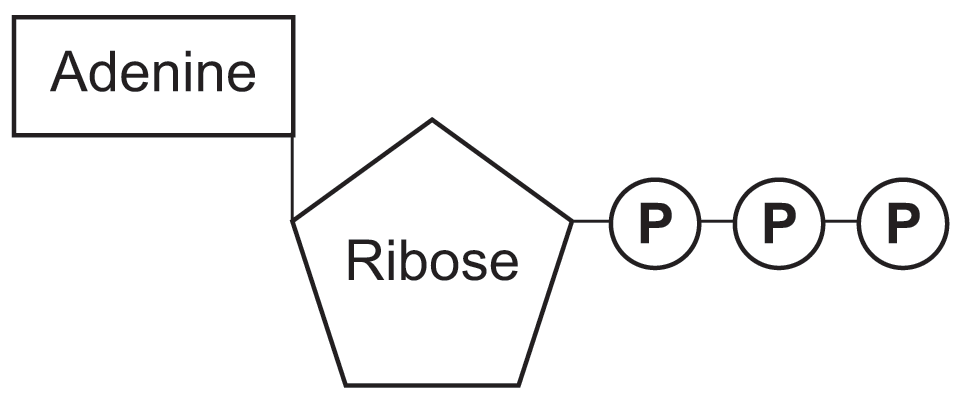
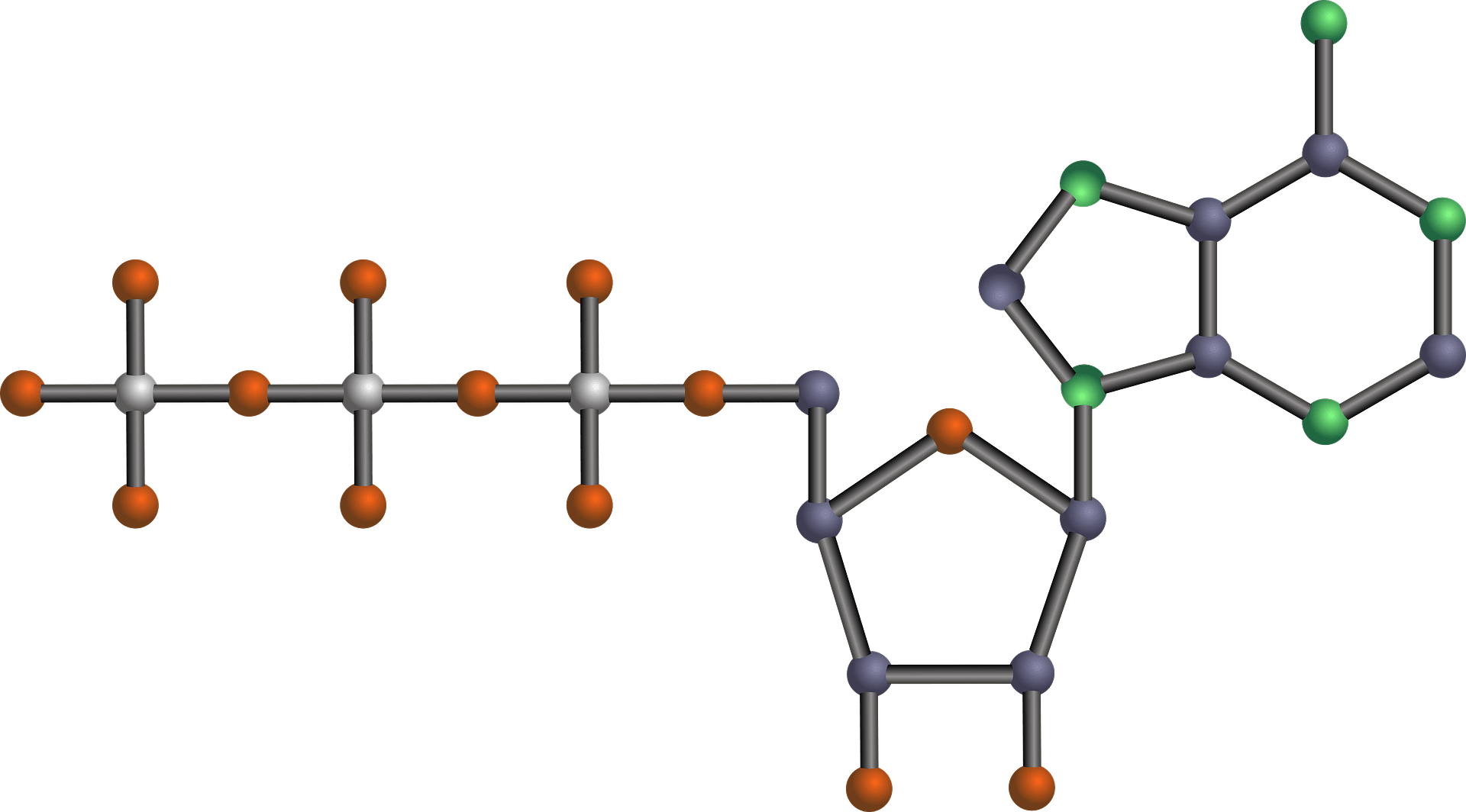
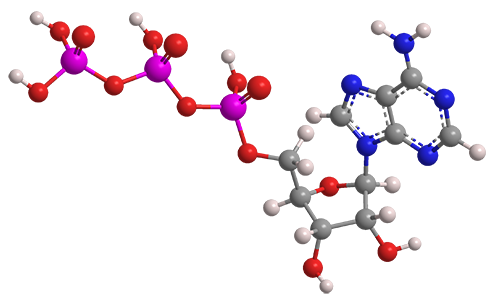
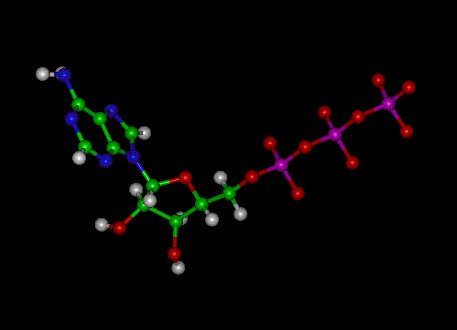
ATP structure + function - Weebly These components are linked together into a single molecule through condensation reactions. Picture. ATP and energy release The ATP molecule in 3-D - BioTopics The ATP molecule - rotatable in 3 dimensions · the base adenine - a double ring like section with several nitrogen atoms (blue), · the 5 carbon sugar ribose in ...
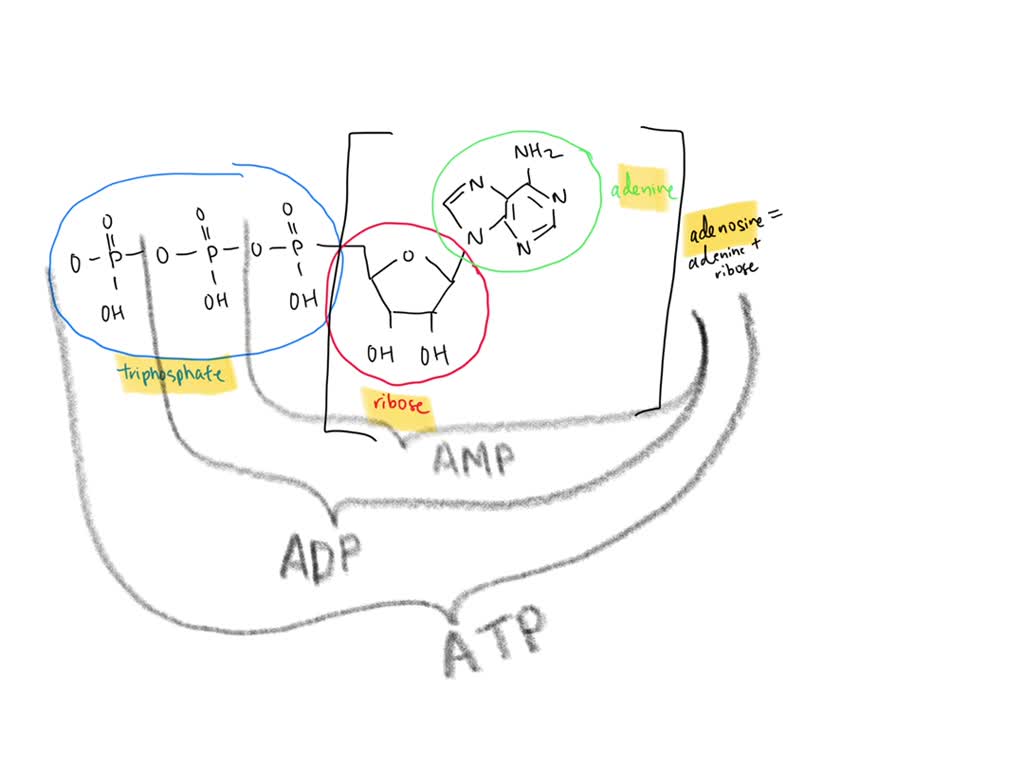
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP … Web30. Juli 2016 · Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical …

Label an atp molecule
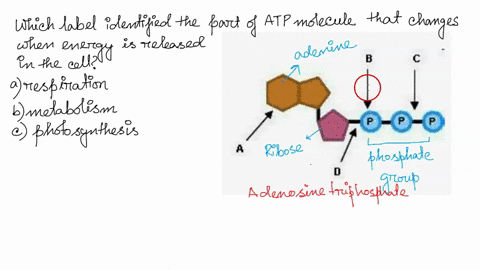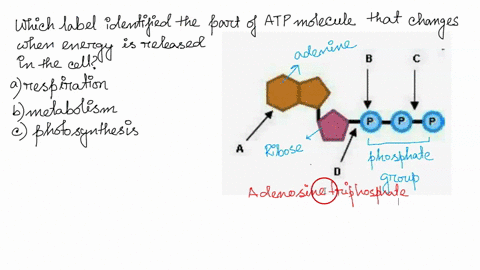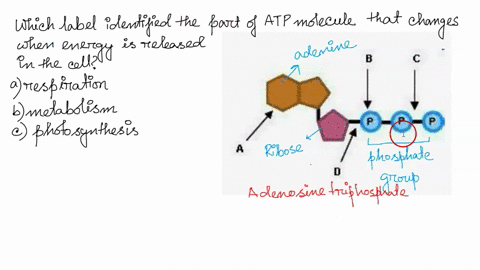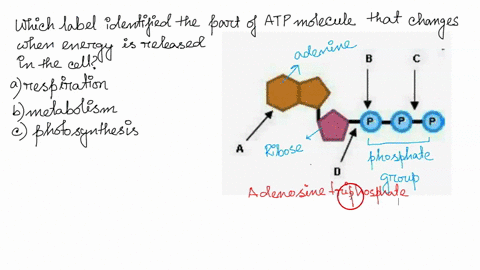
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using … WebQuestion: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. … Model of ATP Molecule - Perkins School for the Blind The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's activities. Understanding the structure of this molecule leads to a clear understanding of the manner in which it provides needed energy to the cell. Label the molecule of ATP. Show where the high energy bond is ... The ATP molecule is comprised of an adenosine molecule attached to three phosphates. The bond with the last phosphate is highly energetic.
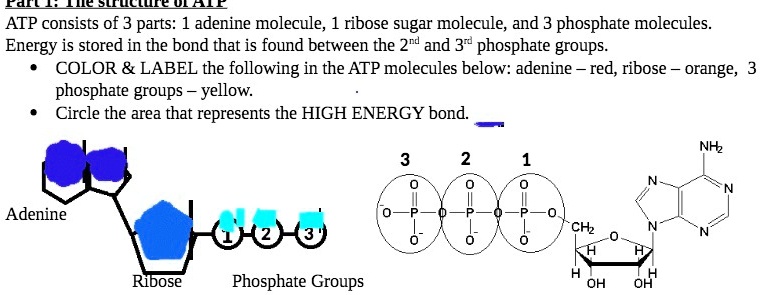
Label an atp molecule. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Oct 4, 2019 · Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor The most important donor of phosphate groups in the cell is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, commonly known by its abbreviation ATP. that there are essentially three parts to the ATP molecule: an adenine nucleoside 'base', a five-carbon sugar (ribose), and triphosphate. The three phosphates are designated by Greek letters a, b, and g ... ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) - Khan Academy Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. Image credit: OpenStax Biology. Adenosine Triphosphate - ATP - Bris.ac.uk The ATP molecule is composed of three components. At the centre is a sugar molecule, ribose (the same sugar that forms the basis of DNA). Attached to one side ...
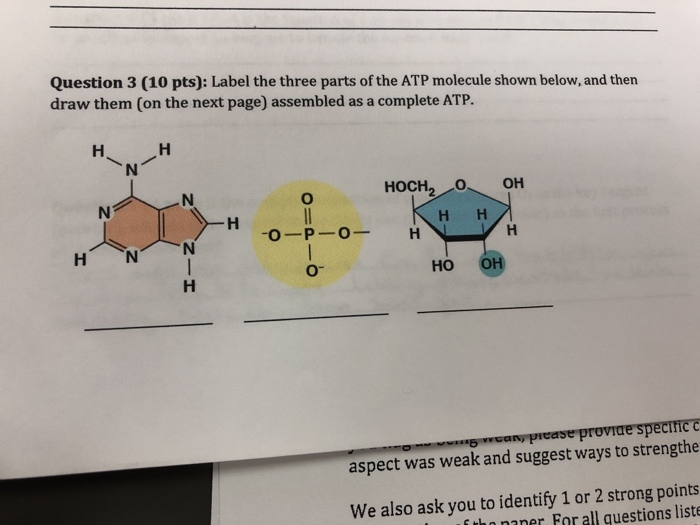
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg Question: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6. 6.4: ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate - Biology LibreTexts The molecular structure of adenosine triphosphate is shown. Three phosphate groups are attached to a Figure 6.4.1: ATP is the primary energy ... Oxidative phosphorylation | Biology (article) | Khan Academy 30-32 ATP from the breakdown of one glucose molecule is a high-end estimate, and the real yield may be lower. For instance, some intermediates from cellular respiration may be siphoned off by the cell and used in other biosynthetic pathways, reducing the number of ATP produced. Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (8 ratings) Transcribed image text: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. NH, Answer Bank guanine three phosphate groups v=CH deoxyribose adenine -O-P-0 - P-0 — -0-CH ribose k H H two phosphate groups ОН ОН.
ATP: Definition, Structure & Function | StudySmarter WebATP or adenosine triphosphate is the energy-carrying molecule essential for all living organisms. It is used to transfer the chemical energy necessary for cellular processes. … 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor Web20. Juli 2022 · The most important donor of phosphate groups in the cell is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, commonly known by its … Biology ATP Flashcards | Quizlet chemical bonds (in phosphate groups) What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? 1. Adenine 2. Phosphate Groups 3. Ribose Write the reaction for the breakdown of ATP. ATP -> <- ADP + Pi Write the equation for photosynthesis. Sunlight + Carbon Dioxide + Water -> Glucose + Oxygen 1. Label the parts of the ATP molecule using the word bank. What is formed when you break a bond between phosphate groups in ATP? 4. How many TOTAL molecules of ATP are produced during the process of cellular respiration ...
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? - Toppr ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is ...
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet WebAdenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine. …
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers Web18. Dez. 2013 · The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate …
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts small organic molecules including adenosine triphosphate ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps.
What are the three parts of an ATP molecule - Quizlet What are the 3 parts of an ATP molecule adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups Energy is released from ATP when a phosphate is removed Organisms such as plants that make there own food are called autotrophs Plants gather energy with light-absorbing molecules called pigments Most plants appear green because chlorophyll doesn't absorb green light
ATP: How It Works, How It's Made, and Why It's Important Web4. Nov. 2022 · ATP is made of a nitrogen base (adenine) and a sugar molecule (ribose), which create adenosine, plus three phosphate molecules. If adenosine only has one …
PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced ... 5 (a) Fig. 5.1 is a diagram of an ATP molecule. Label Fig. 5.1 to show the structure of an ATP molecule. Fig. 5.1 [3] (b) Statements A, B, C and D are part of the sequence of events that occur during the loading of sucrose into a phloem sieve tube. A hydrogen ions bind to co-transporter protein B diffusion of sucrose via plasmodesmata
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Web20. Jan. 2017 · Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, …
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. Energy is released by hydrolysis of the third phosphate group.
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis.Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer.
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine Classify the following statements about the structure of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule as true or false. Reminder: Adenosine diphosphate is abbreviated ADP.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Web22. Nov. 2016 · Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: …
Adenosine triphosphate - American Chemical Society Adenosine 5′-triphosphate, abbreviated ATP and usually expressed without the 5′-, is an important “energy molecule” found in all life forms.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Nov 22, 2016 · Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link
Chapters 5b - 7 Honors Biology Flashcards | Quizlet ATP contains energy which can then be used to do other functions in cells such as transport work, mechanical work, and chemical work. The number of ATP's that are produced in: 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain 4. Fermentation 5. Total in the 3 phsases of Cellular respiration 1. 2 ATP 2. 2 ATP 3. 28 ATP 4. 0-2 ATP 5. 32 ATP
Label the molecule of ATP. Show where the high energy bond is ... The ATP molecule is comprised of an adenosine molecule attached to three phosphates. The bond with the last phosphate is highly energetic.
Model of ATP Molecule - Perkins School for the Blind The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's activities. Understanding the structure of this molecule leads to a clear understanding of the manner in which it provides needed energy to the cell.
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using … WebQuestion: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. …











![Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP ...](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/887889_ba7e3b5cc09d418996079c2f5db4b569.png)











Post a Comment for "45 label an atp molecule"