39 nucleus electron micrograph labelled
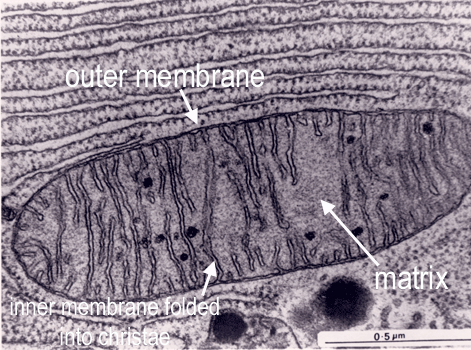
Cell Biology - Buffalo Public Schools microscope was invented – the electron microscope. ... nucleus and membrane-bound cellular organelles. The ... Write on or label the final drawing in. IB DP Biology 1.2 Ultrastructure of cells Question Bank SL Paper 1 What is the structure labeled X in the electron micrograph of a rat liver cell? A. Ribosome B. Lysosome C. Mitochondrion D. Nucleus. Answer/Explanation Markscheme. C. Examiners report. There were comments from some teachers about the electron micrograph used in this question. The mitochondrion that candidates had to identify has a sigmoid shape ...
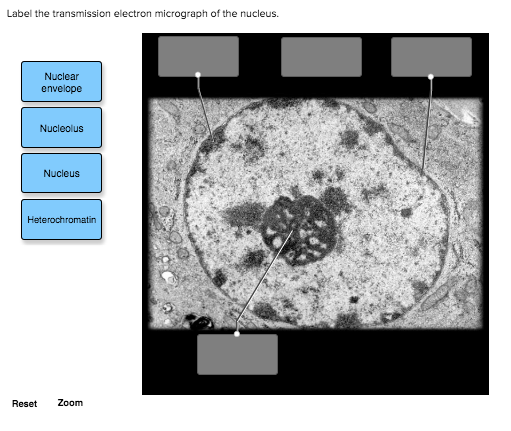
Solved Label the transmission electron micrograph of the - Chegg Label the transmission electron micrograph of the cell. 0 Nucleus rences Mitochondrion Heterochromatin Peroxisome Vesicle ULAR bumit Click and drag each label into the correct category to indicate whether it pertains to the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane.

Nucleus electron micrograph labelled
101 Electron Micrograph Nucleus Premium High Res Photos - Getty Images Browse 101 electron micrograph nucleus stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. neuron cell close-up view - electron micrograph nucleus stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. Biology: 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells Flashcards | Quizlet What is the structure labeled X in the electron micrograph of a rat liver cell? A. Ribosome B. Lysosome C. Mitochondrion D. Nucleus C. Mitochondrion The image shows a phagocytic white blood cell as seen with a transmission electron microscope. Which features can be both within this cell and in a photosynthetic bacterium? A. Chloroplasts Plant Cell: Definition, Types of Plant Cells and More - Embibe Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. These differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined under an electron microscope. Observe the labelled diagram of plant cell structure as given below:
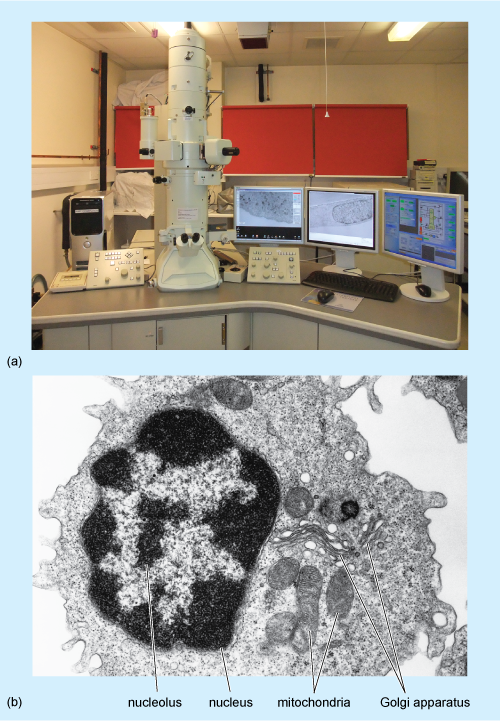
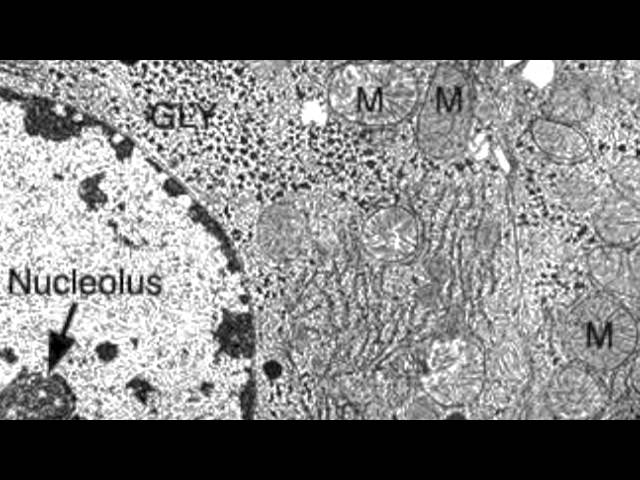
Nucleus electron micrograph labelled. Electron Micrographs Electron Micrographs** ... Figure 2 Micrograph of a portion of a nucleus: ... The two unit membranes making up this gap junction are labelled C. 1.2 Skill: Interpretation of electron micrographs - YouTube Dec 25, 2015 ... Interpretation of electron micrographs to identify organelles and deduce the functions of specialized cells. Electron micrographs used with ... Electron Micrographs of Cell Organelles | Zoology - Biology Discussion The Electron Micrograph of Nucleus: This is an electron micrograph of nucleus. (Fig. 17 & 18): (1) Nucleus was discovered by Brown (1831). (2) It is a characteristic entity of almost all eukaryotic cells except mammalian RBCs. (3) The nucleus is generally one but may also be two, four or many. IB DP Biology Topic 1: Cell biology 1.2 Ultrastructure of cells Study Notes The electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create an image of the specimen. It is capable of much higher magnifications and has a greater resolving power than a light microscope, allowing it to see much smaller objects in finer detail.
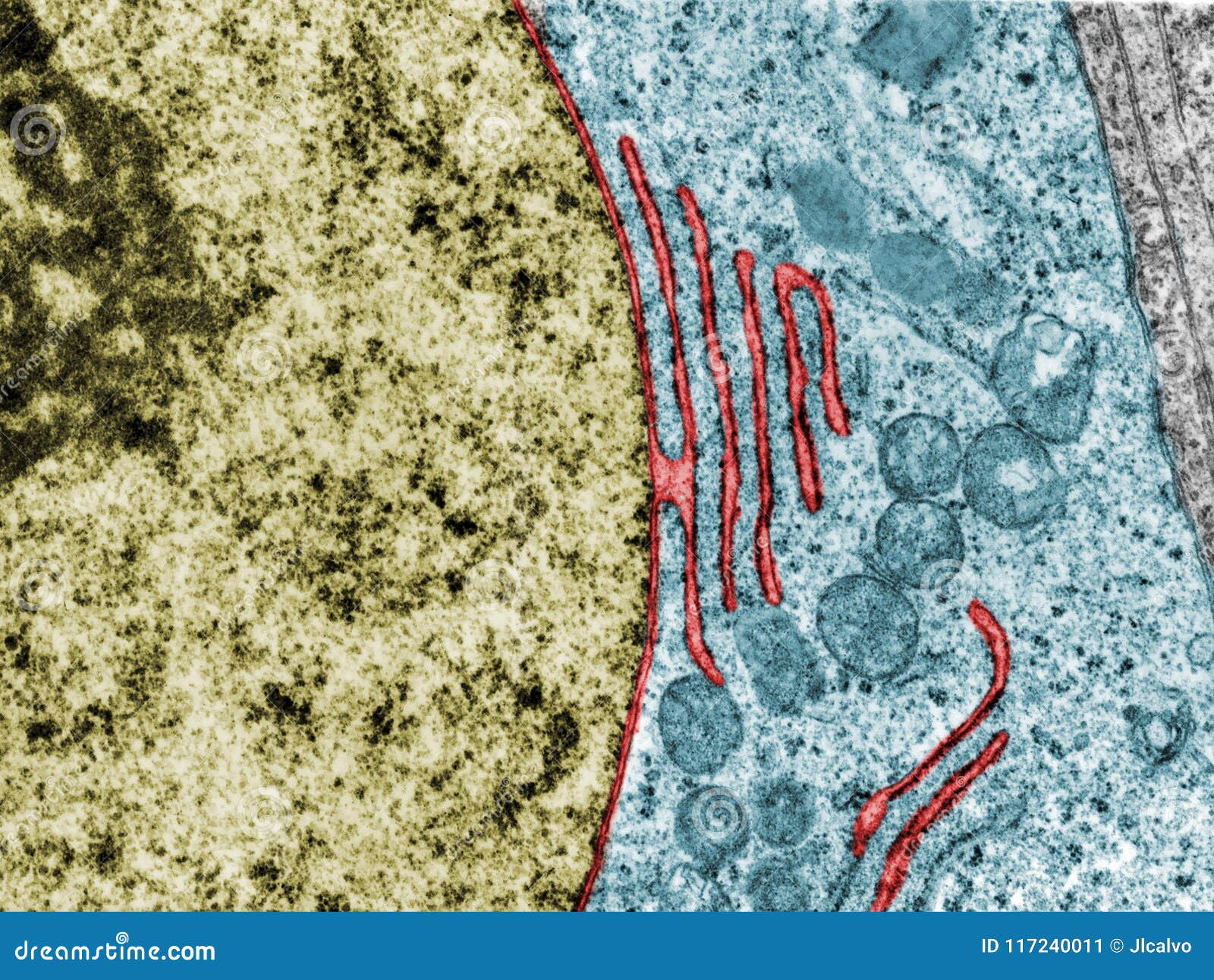
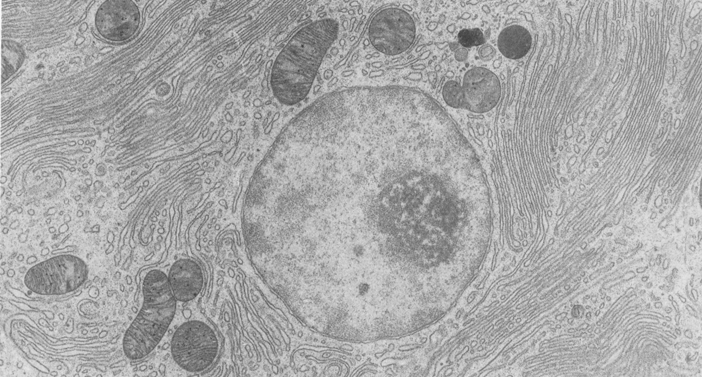
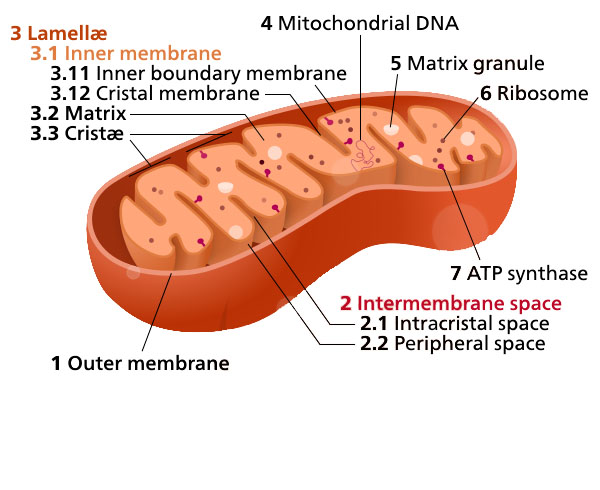
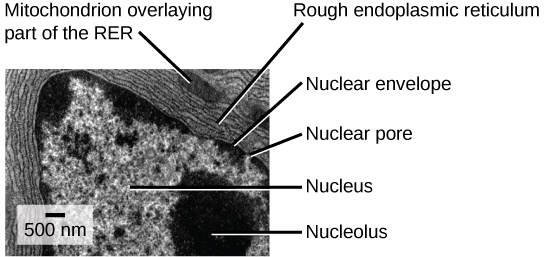
Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I - Lumen Learning The centrosome is a region near the nucleus of animal cells that functions as a microtubule-organizing center. It contains a pair of centrioles, two structures that lie perpendicular to each other. ... (Figure 8). Electron microscopy has shown that ribosomes consist of large and small subunits. Ribosomes are enzyme complexes that are ... Electron microscopes - Cell structure - Edexcel - BBC Bitesize the scanning electron microscope (SEM) has a large depth of field so can be used to examine the surface structure of specimens TEMs have a maximum magnification of around ×1,000,000, but images... The Cell: The Histology Guide - University of Leeds An electron micrograph of a nucleus Types of Nucleus Cells are normally diploid - this means that they have a pair - two sets of homologous chromosomes, and hence two copies of each gene or genetic locus. However, cells can be haploid, polyploid or aneuploid. Haploid: only has one set of chromosomes - i.e. in a sperm or oocyte. 3.6B: The Endoplasmic Reticulum - Medicine LibreTexts The membrane of the ER, which is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins, is continuous with the nuclear envelope. Rough ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: This transmission electron micrograph shows the rough endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles in a pancreatic cell.
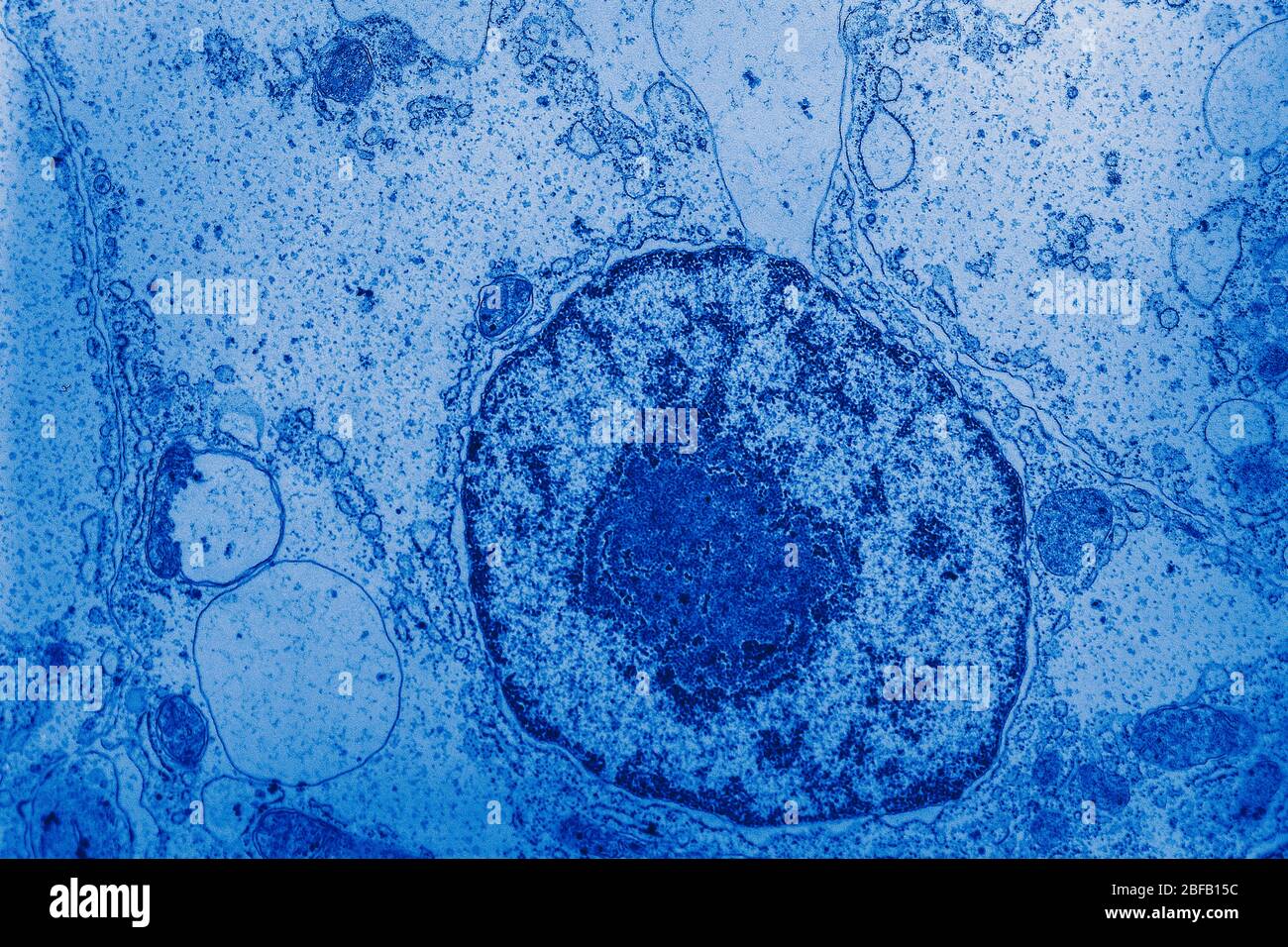
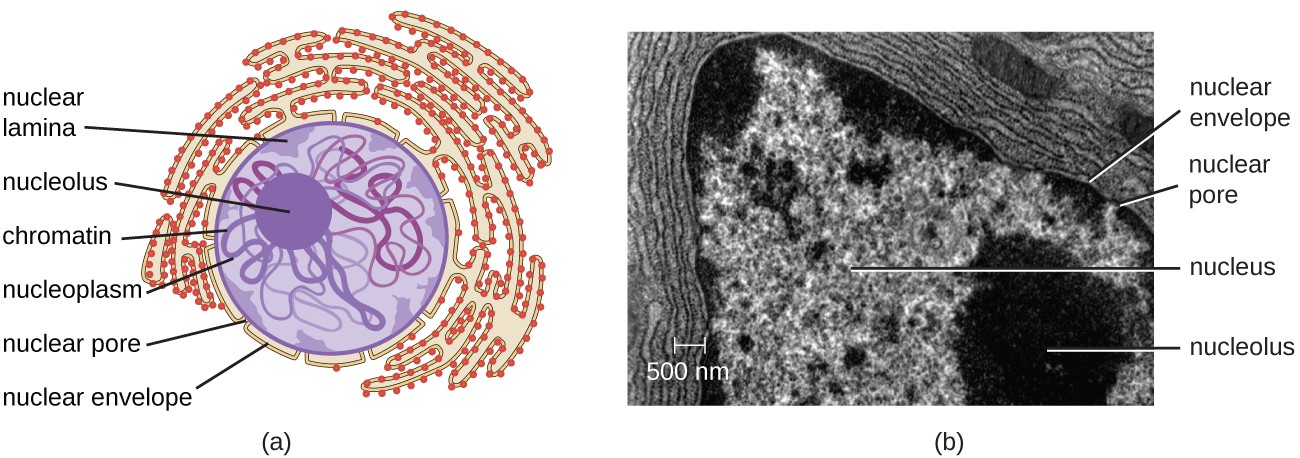
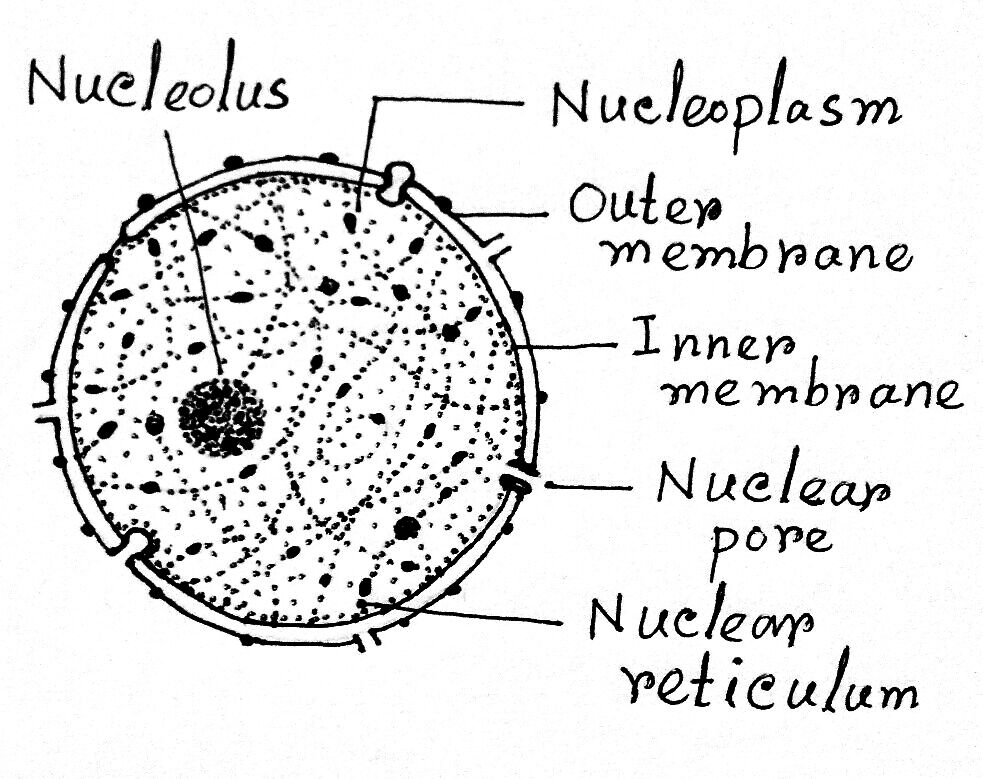
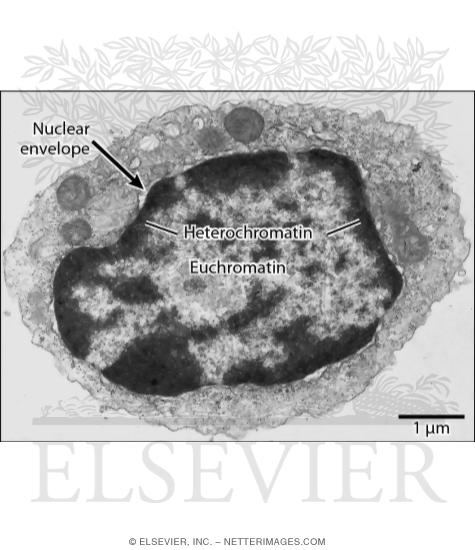
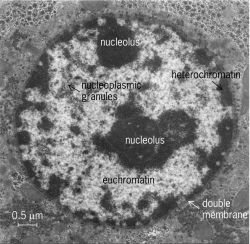
Solved Please label the electron micrograph to assess your - Chegg Please label the electron micrograph to assess your knowledge of the structure and function of a cell's nucleus nuclear pore endoplasma reticulum chromatin nucleolus nuclear envelope This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Virtual EM Micrograph List | histology - University of Michigan 021. Plasma Cell: This electron micrograph shows a typical secretory cell, a plasma cell, which secretes immunoglobulin protein. Many of the major types of cellular organelles are visible in this image. In the nucleus, areas of euchromatin and heterochromatin can easily be identified. Virtual Slide. Cell Nucleus - function, structure, and under a microscope The nucleus is a specialized organelle that contains double-layer membranes with pores. The main function of the nucleus is to govern cell activities and to carry genetic information to pass to the next generation. This is why we call the nucleus the brain of the cells. [In this figure] The cell nucleus diagram and its structure. Nuclear Labeling | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Labeling the nucleus typically relies on some type of dye that binds nucleic acids, and depending on how much distinction you need between DNA and RNA and whether or not the cells you're labeling are live or fixed, your choice of stains will vary.
Nucleus- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Diagram The nucleus is the organelle that houses chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of DNA, which contains heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. Chromosomes are present in the form of strings of DNA and histones (protein molecules) called chromatin.
4.3 Eukaryotic Cells - Biology 2e | OpenStax Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.".
Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Label the transmission electron micrograph of the mitochondrion. Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes
A tour of the cell: View as single page - The Open University (b) A transmission electron micrograph of a frog leukocyte (white blood cell). ... The nuclei are labelled pink, microtubules (composed of the protein ...
Neuron under Microscope with Labeled Diagram - AnatomyLearner The nucleus is the spherical or elliptical structure in the neuron containing euchromatic staining (pale staining). Again, the shape of the nucleus of a neuron is generally large because of the little cell body cytoplasm. There is a prominent nucleolus evident in the nucleus of a neuron.
The Cell Nucleus: A Brief Overview - Microscope Clarity The discovery of electron microscopy was critical in defining the double layered nuclear membrane, nuclear lamina, chromatin packing and nuclear pore complexes. Remarkably, many features of the nucleus including organisation and regulation of genetic material were only elucidated in the 50 years, with new discoveries continuing to be made every ...
Electron Microscope Principle, Uses, Types and Images (Labeled Diagram ... As the name suggests, an electron microscope utilizes a beam of accelerated electron to illuminate the sample to be viewed. Built first in 1931, the electron microscope was built by a German academician and engineer Ernst Ruska and the same principles continue to be the basic structures for modern day electron microscopes.
Electron Microscopic Structure of a Typical Bacterial Cell The characteristic of a bacterial nucleus is the absence of nuclear membrane, nucleolus, chromonemata and nuclear sap. Such a nucleus is termed as nucleoid or genophore. Under electron microscope the nucleoid appears to be fibrillar and composed of a double or single stranded DNA.
Electron Micrographs - University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center micrographs with labelled subcellular structures that you should be able to identify. Also, be sure to observe any electron micrographs which are made available in the laboratory by the instructor. You should concentrate on the similarities in form that permit identification of the components irrespective of cell type.
Nucleus - Definition, Structure & Function, Cellular vs Atomic Nuclei The atomic nucleus, on the other hand, lacks the membrane or pores. Rather, the neutrons and protons are tightly packed and thus occupy a very small space in the atom. · Size - As compared to the cellular nucleus that takes up about a tenth of the entire cell volume, the atomic nucleus is significantly small.
Looking at the Structure of Cells in the Microscope - NCBI Bookshelf The cell wall, nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes are easily visible in this transmission electron ...
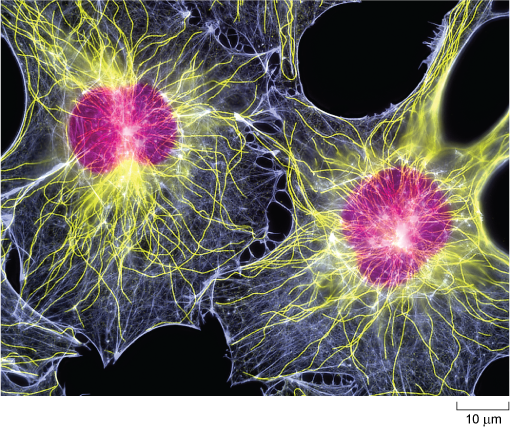
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: Animal Cell Structure The nuclei are stained with a red probe, while the Golgi apparatus and microfilament actin network are stained green and blue, respectively. The microscope has been a fundamental tool in the field of cell biology and is often used to observe living cells in culture.
Cell Micrographs | BioNinja A micrograph is a photo or digital image taken through a microscope to show a magnified image of a specimen While organelles have identifying structures, specific shapes may vary depending on the location of cross-sections Prokaryotic Cell Features Feature: none nucleoid cell wall pili flagella all Eukaryotic Cell Features
Electron micrograph of epoxy resin section of part of a nucleus with a... Third, immunogold labelling coupled with electron microscopy provides sufficient resolution to distinguish where label is relative to the different nucleolar ...
Electron microscopes - Cell structure - Edexcel - BBC Bitesize Electron microscopes use a beam of electrons instead of beams or rays of light. Living cells cannot be observed using an electron microscope because samples are placed in a vacuum. There are two ...
DP Biology (Cells: 1.1, 1.2, 1.5, 6.3) Quiz - Quizizz answer choices chloroplasts multiple nuclei 70s ribosomes lysosomes Question 2 30 seconds Q. The image shows an electron micrograph of a fungus, Candida albicans. Which terms identify the structures labelled I and II in the image? answer choices I: cell membrane; II: vescicle I: cell wall; II: chloroplast I: plasma membrane; II: mitochondrion
Cell structure - Oxford University Press Identify the following structures from an electron micrograph: ... known that there are no cells in dead cork, the modern term 'cell' comes from this label.
Microscopy: Intro to microscopes & how they work (article) - Khan Academy In most cases, the part of a cell or tissue that we want to look at isn't naturally fluorescent, and instead must be labeled with a fluorescent dye or tag before it goes on the microscope. The leaf picture at the start of the article was taken using a specialized kind of fluorescence microscopy called confocal microscopy.
Plant Cell: Definition, Types of Plant Cells and More - Embibe Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. These differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined under an electron microscope. Observe the labelled diagram of plant cell structure as given below:
Biology: 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells Flashcards | Quizlet What is the structure labeled X in the electron micrograph of a rat liver cell? A. Ribosome B. Lysosome C. Mitochondrion D. Nucleus C. Mitochondrion The image shows a phagocytic white blood cell as seen with a transmission electron microscope. Which features can be both within this cell and in a photosynthetic bacterium? A. Chloroplasts
101 Electron Micrograph Nucleus Premium High Res Photos - Getty Images Browse 101 electron micrograph nucleus stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. neuron cell close-up view - electron micrograph nucleus stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images.










![PDF] Electron-microscope observations on cell nuclei in ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/cbf065cf56ecafebbf501a366b02ccbe35e280ec/2-Figure1-1.png)




Post a Comment for "39 nucleus electron micrograph labelled"