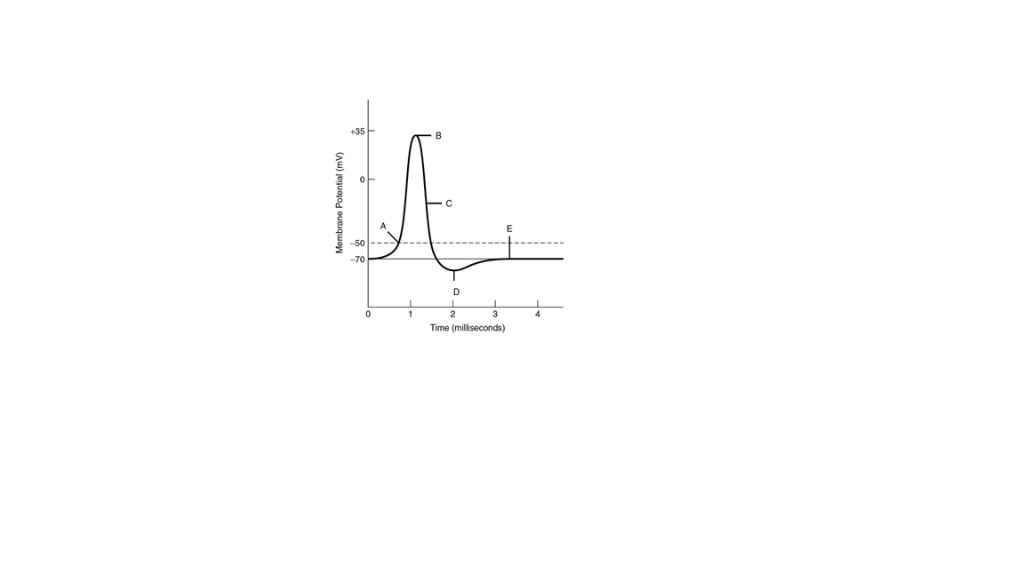
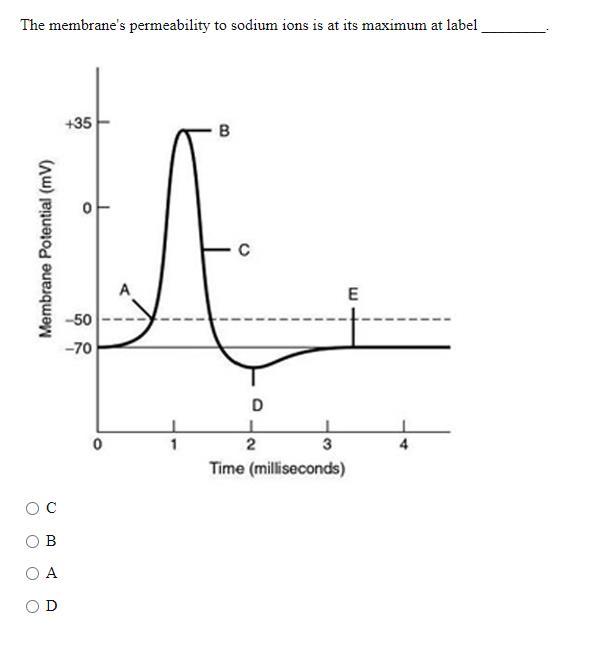
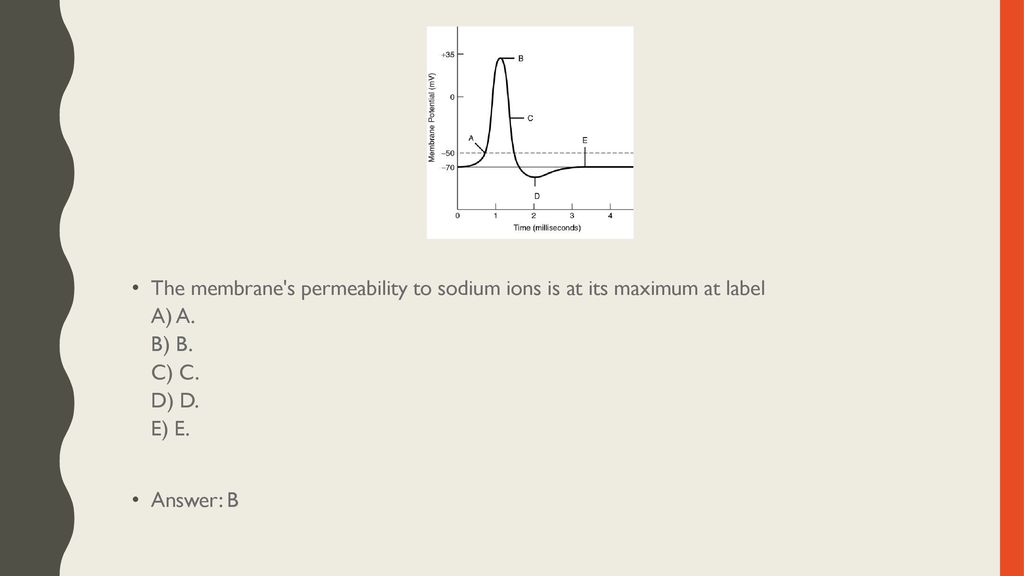
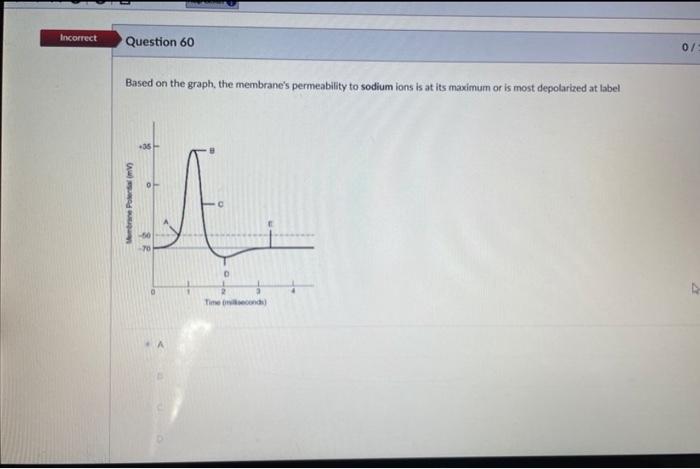
38 the membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest
Why are the cell membranes of neurons and nerves more permeable ... - Quora Answer (1 of 4): By way of ion channels, nerve cells are able to perform their functions. These channels pump K+ into the nerve cells, kicking Na+ out, so, essentially, they work against each other. When the potassium channels open, the potassium rushes in, making the cell more positive, which th... Chapter 48 Mastering: Nervous System Part 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Membrane potential K+ False The potential energy of a membrane potential comes bth from the difference in electrical charge and from the concentration gradient of ions across a membrane. Potassium leak channel K+ ions flow along their concentration gradient to maintain the resting potential of a neuron.
If the permeability of a resting axon to sodium ion 12)If the permeability of a resting axon to sodium ion increases, 12) A) outward movement of sodium ion will decrease.B)the membrane potential will hyperpolarize. C)inward movement of sodium will increase and the membrane will depolarize. D)the membrane potential will repolarize. E)inward movement of sodium ion will increase. E )
The membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest
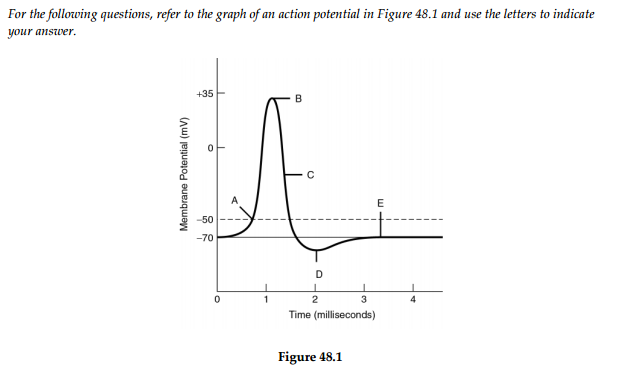
Cell Membrane Transport: Selective Permeability & Types This biochemical composition results in the plasma membrane being permeable to some compounds but not others, otherwise considered selective permeability. Transport of many solutes across this... Bio Test #3 Flashcards | Quizlet The membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest at label _____. a) A b) B c) C d) D. b) B. 53) Refer to the following graph of an action potential to answer the question. ... a decrease in the membrane's permeability to potassium and chloride ions. b) the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels and the invactivation of sodium ... Membrane potential: Definition, equilibrium, ions | Kenhub Cell membrane permeability The third factor that affects the membrane potential is the permeability of the membrane for the sodium and potassium, which depends on the ion channels. Ion channels are specialized proteins of the cell membrane that enable migration of the ions. There are two types of ion channels:
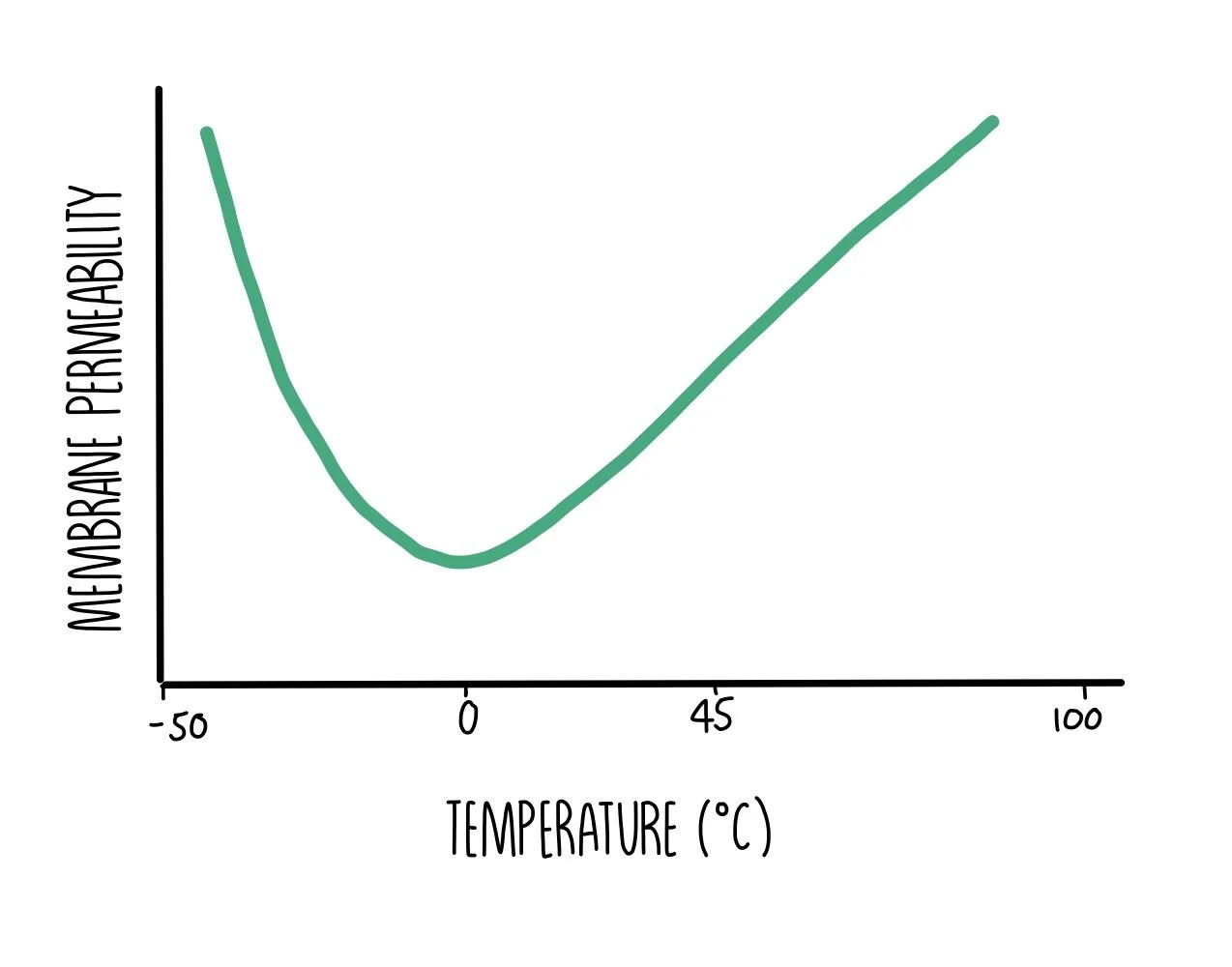
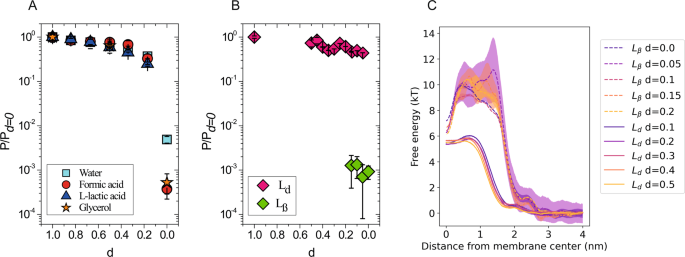
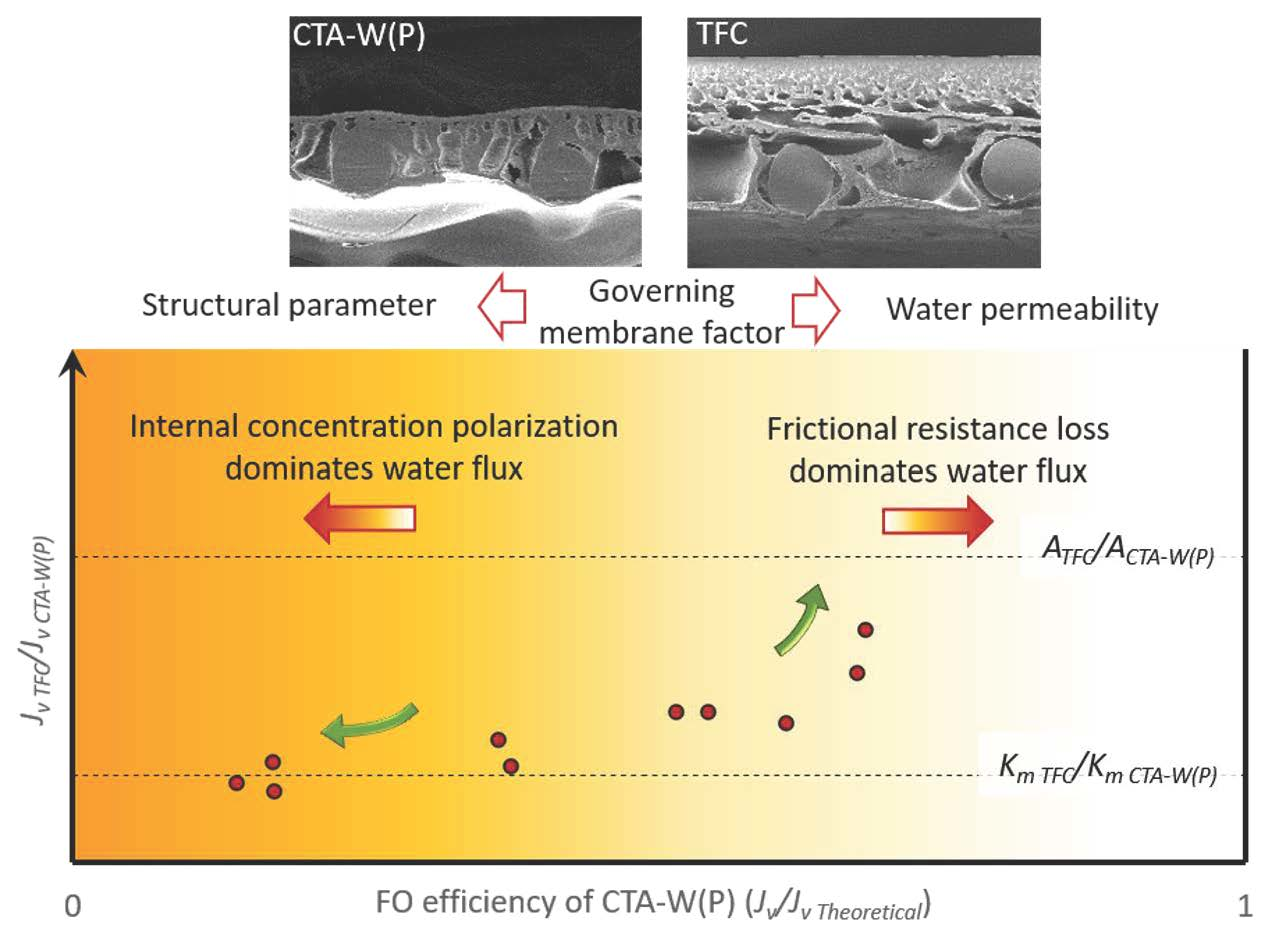
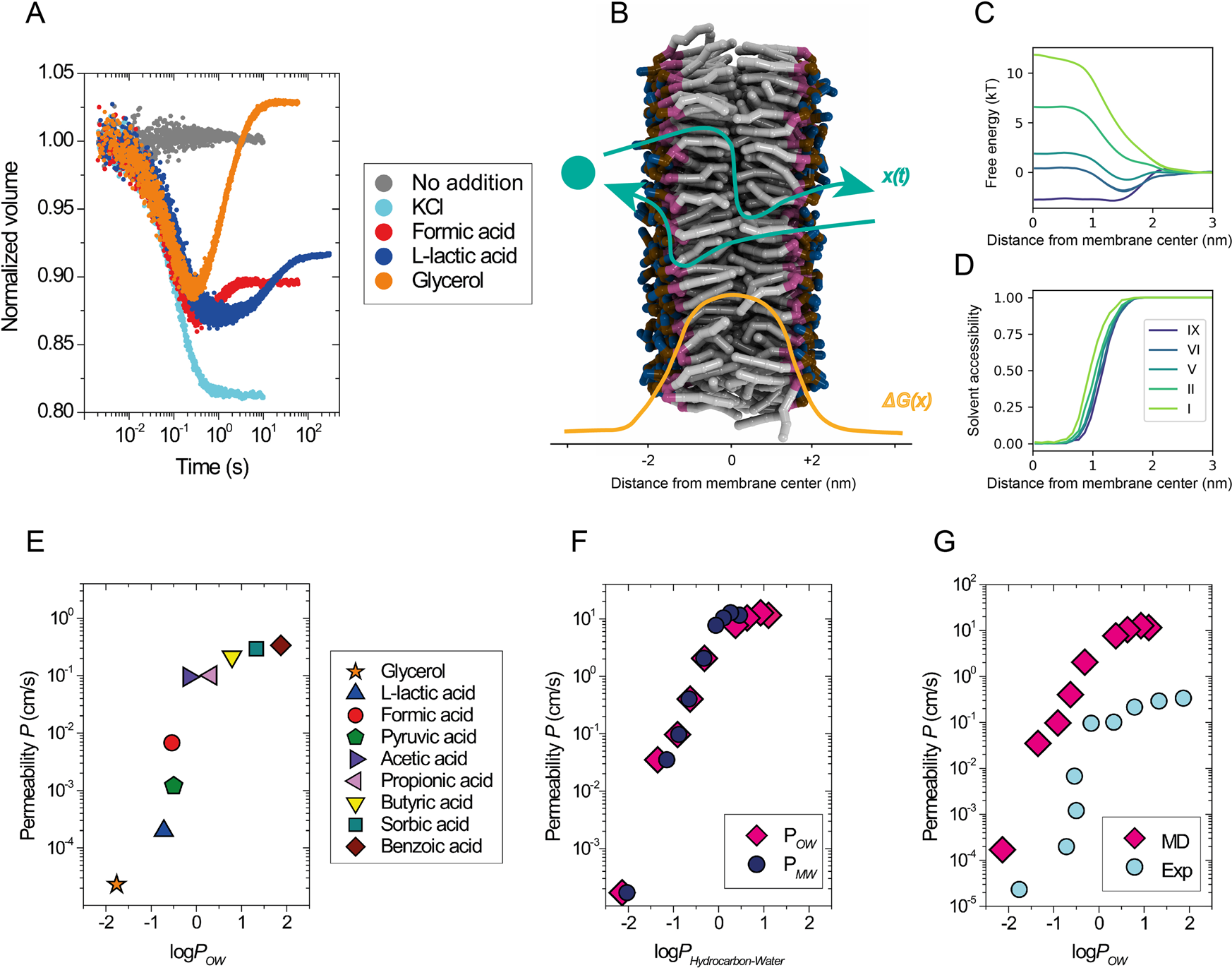
The membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest. If a resting axon increases its permeability to - Course Hero 10) If a resting axon increases its permeability to sodium ions: A) the membrane potential will repolarize. B) the membrane potential will hyperpolarize. C) the influx of sodium ions will increase and the membrane will depolarize. D) the outward movement of sodium ions will decrease. » What is the permeability of the cell membrane? The permeability of the cell membrane to glycerol is p≈10-100 nm/s (BNID 110824) as can be read from Figure 1. The time scale for a glycerol molecule inside the cell to escape back to the surrounding medium, assuming no return flow into the cell (c out =0), can be crudely estimated by noting that the efflux from the cell is p·A·c in where A ... Chapter 37 Flashcards | Quizlet The "threshold" potential of a membrane the minimum depolarization needed to operate the voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels action potential move along axons more rapidly in myelinated than in nonmyelinated axons toxin that binds specifically to voltage-gated sodium channels in axons prevent the depolarization phase of the action potential Cell Membrane Permeability - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The best example of alteration of membrane permeability can be derived from the peptide antibiotic bacitracin of B. licheniformis. 56 Initially, a complex of a metal ion with isoprenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) is formed near the cell membrane and later it tries to cross the membrane. Bacitracin, by binding with IPP, prevents its dephosphorylation ...
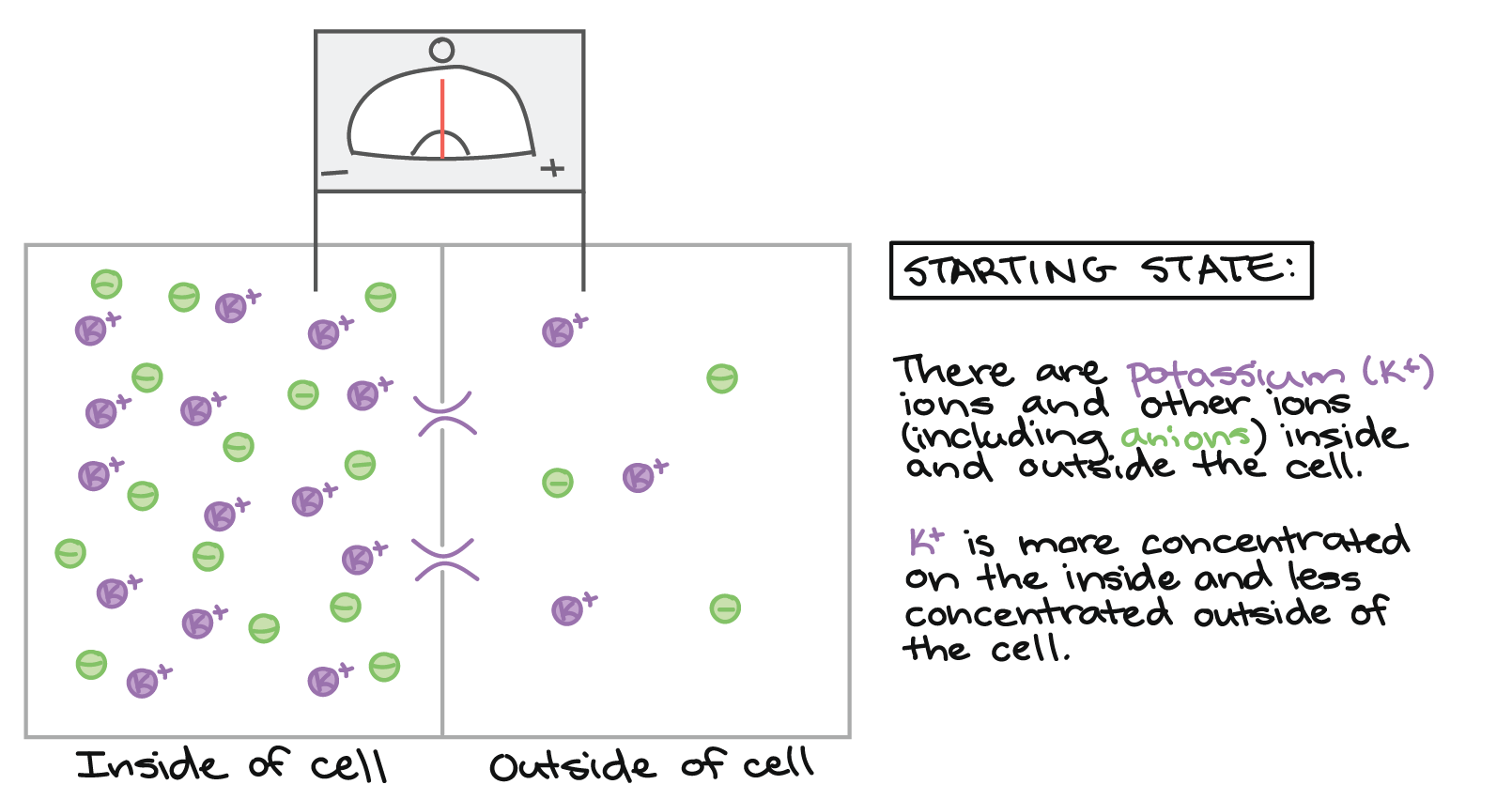
What is membrane permeability? - Answers May 09, 2015 · See answer (1) Best Answer. Copy. Membrane permeability refers to the ability of molecules, substances, etc. to pass through the membrane. For example, the cell membrane is referred to as 'semi ... MEMBRANE POTENTIAL Test Questions Flashcards | Quizlet Predict the effect on the resting membrane potential if permeability of cell membrane to sodium ions increases. A)When the permeability to sodium ions increases, the sodium ions diffuse into the cell and the inside of the cell becomes more positive, resulting in depolarization. B)When the permeability to sodium ions increases, the sodium ions diffuse out of the cell and the inside of the cell becomes more negative, resulting in depolarization. CV Physiology | Membrane Potentials During an action potential, the cell membrane become more permeable to Na +, which increases sodium entry into the cell through sodium channels . At the peak of the action potential in a cardiac cell (e.g., ventricular myocyte), the membrane potential is approximately +20 mV. Solved Describe the permeability of the axon membrane to - Chegg Best Answer. ANS--> THE AXON MEMBRANE is permeable to both Na+ and K+ • ATP is used to power a potassium/sodium ion pump, pushing the sets of ions back to their original sides, returning the axon to its resting pot …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Describe the permeability of the axon membrane to ions during repolarization.
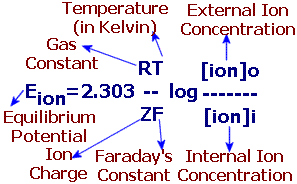
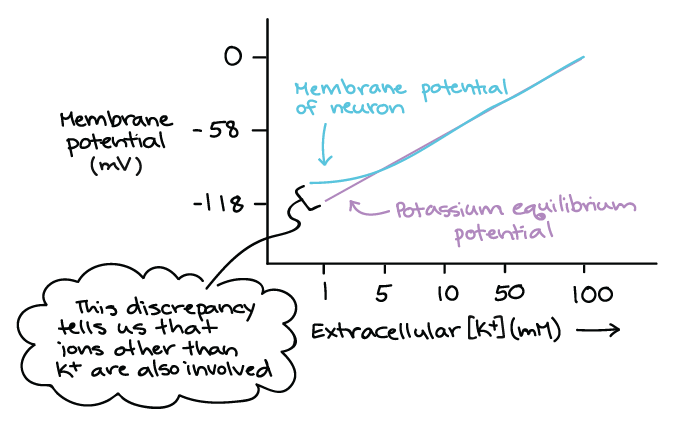
Bio II Chapter 48 Flashcards | Quizlet 7) Although the membrane of a "resting" neuron is highly permeable to potassium ions, its membrane potential does not exactly match the equilibrium potential for potassium because the neuronal membrane is also ________. A) slightly permeable to sodium ions 8) The operation of the sodium-potassium pump moves ________. Membrane potential - Definition, Types, Equilibrium and Ions If we introduce one electrode inside the axon and one to the cytoplasmic surface of the axon, hyperpolarization (in the case of negative internal electrodes) or depolarization (in the case of negative external) occurs. If we increase the membrane potential to the threshold potential (in membrane with resting membrane potential, from -70mV to about ... What happens if the permeability of a resting axon to sodium ion ... Low calcium levels in the extracellular fluid increase the permeability of neuronal membranes to sodium ions, causing a progressive depolarization, which increases the possibility of action... Membrane potential: Definition, equilibrium, ions | Kenhub Cell membrane permeability The third factor that affects the membrane potential is the permeability of the membrane for the sodium and potassium, which depends on the ion channels. Ion channels are specialized proteins of the cell membrane that enable migration of the ions. There are two types of ion channels:
Bio Test #3 Flashcards | Quizlet The membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest at label _____. a) A b) B c) C d) D. b) B. 53) Refer to the following graph of an action potential to answer the question. ... a decrease in the membrane's permeability to potassium and chloride ions. b) the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels and the invactivation of sodium ...
Cell Membrane Transport: Selective Permeability & Types This biochemical composition results in the plasma membrane being permeable to some compounds but not others, otherwise considered selective permeability. Transport of many solutes across this...

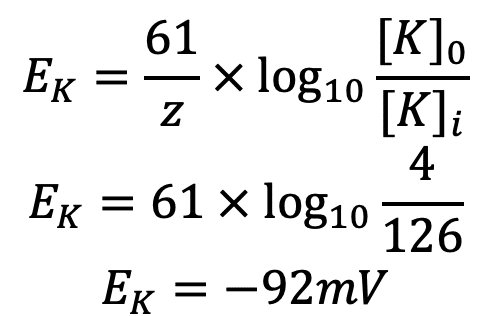















Post a Comment for "38 the membrane's permeability to sodium ions is greatest"