38 transverse wave with labels
Examples, Speed & Reflection of a Transverse Waves - BYJUS In Physics, a transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A simple demonstration of the wave can be created on a horizontal length of the string by securing one end of the string and moving the other up and down. BYJUS BYJUS
Label A Wave Worksheets & Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw by Geo-Earth Sciences 48 $1.50 PDF Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw Review/Reinforcement/Practice Activity for students to define parts of a transverse wave and illustrate waves using standard measurements. Great practice activity or test review exercise.

Transverse wave with labels
Transverse and longitudinal waves - Properties of waves - BBC Examples of transverse waves include: ripples on the surface of water; vibrations in a guitar string; a Mexican wave in a sports stadium; electromagnetic waves, eg light waves, microwaves, radio ... Answered: Name:\iana Zomorai 1. The illustration… | bartleby Label each part in the space provided. a. b. a. e. g.1 of Fill in the blanks: from one place to another. trough 2. Waves carry while the lowest part is the 3. The highest point on a transverse wave is the 4. The Crest is the height of the wave. 5. The distance from one crest to the next is the Wevelegth 6. Below are a number of series of waves. Transverse wave - Wikipedia Transverse waves commonly occur in elastic solids due to the shear stress generated; the oscillations in this case are the displacement of the solid particles away from their relaxed position, in directions perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. These displacements correspond to a local shear deformation of the material.
Transverse wave with labels. Transverse Wave: Definition, Parts & Examples - Study.com There are various features we can label on a transverse wave, as shown here: A crest (or peak) of a wave is one of the top-most parts, as high as the wave goes. A trough is the lowest part, as low... What Are the Parts of a Transverse Wave? - Reference.com A transverse wave is one in which the energy of the wave displaces particles perpendicular to the energy wave. For instance, a ripple on a pond moves the water up and down, while the energy moves horizontally across the water. Springs moving up and down and vibrating piano strings are also physical examples of transverse waves. ADVERTISEMENT Transverse Wave Label Lesson Plans & Worksheets Reviewed by Teachers In this types of waves worksheet, students will read 9 types of waves and classify them as either mechanical, electromagnetic, transverse, or compressional waves. Then students will label two wave diagrams with the 8 kinds of waves... + Lesson Planet: Curated OER Waves For Teachers 6th - 8th Students identify the different parts of a wave. transverse wave | Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Diagram ... transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.
Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams - YouTube Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave diagram.This video an... Draw a transverse wave and label it using the word bank below. Draw a transverse wave and label it using the word bank below. - 13806857 Nash2221 Nash2221 24.04.2021 Science Junior High School answered Draw a transverse wave and label it using the word bank below. 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement yzacbaldemoro25 yzacbaldemoro25 Speed of a transverse wave and and Important FAQs - VEDANTU The characteristics of transverse waves are: Transverse waves can only pass through solids and cannot pass through liquids or gasses. Polarization is a phenomenon that can only be observed in transverse waves. The plane of vibration, also known as polarization, is where all the particles in a medium vibrate at the same place. Transverse Waves: Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Formulae Definition of Transverse Waves. When the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave. It travels in a medium in the form of Crests (c) and Troughs (t). The distance between 2 successive crests or 2 successive troughs is known as the Wavelength (λ). Also Read : Wave Optics.
Solved 1. Draw 2 wavelengths of a transverse wave Label the | Chegg.com 1. Draw 2 wavelengths of a transverse wave Label the erest, trough, wavelength, amplitude. 2 Draw a transverse wave with twice the frequency compared to d. 3. A wave is a disturbance that transfers from one place to another. The material that a wave travels through is called its If a wave requires a medium in order to propagate, it is ... Label a transverse wave Diagram | Quizlet Only $2.99/month Label a transverse wave STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Jennifer_Boyes Terms in this set (4) Wavelength the distance from one point on a transverse wave to an identical point on a second wave. The shorter the wavelength the higher the frequency of the wave Peak The highest point of a wave PDF Transverse waves on a string - Harvard University TRANSVERSE WAVES ON A STRING Solutions of the formf(x¡ct) As we saw in Section 2.4,anyfunction of the formf(x ¡ ct) satisfles the wave equation. There are two reasons why this functional form works. The flrst reason, as we showed in Eq. (2.97), is that if you simply plugˆ(x;t) =f(x¡ ct) into the wave equation in Eq. 10 Best Examples of Transverse Waves In Real Life - RankRed What Is A Transverse Wave? When you picture a wave in your mind, you probably envision a squiggly line with peaks and valleys. This is exactly what a transverse wave looks like. It's a moving wave that oscillates perpendicular to the direction of its propagation. Transverse waves can be electromagnetic or mechanical in nature.
label the parts of transverse wave - scholarsqatar.com label the parts of transverse wave. Our services run deep and are backed by over ten years of experience. Your service title Give us a brief description of the service that you are promoting. Try keep it short so that it is easy for people to scan your page. Your service title ...
Transverse waves - Waves - AQA Synergy - GCSE Combined Science ... - BBC Transverse waves are often demonstrated by moving a rope rapidly up and down. In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right....
Label & Draw Transersve Waves: Amplitude, Frequency ... - YouTube Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn h...
Label a Transverse Wave - Labelled diagram Ziehen die Pins an die richtige Stelle auf dem Bild.. Wavelength, Amplitude, Trough, Crest.In nur einer Minute interaktives Unterrichtsmaterial erstellen
Label Parts Of A Wave Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw by Geo-Earth Sciences 49 $1.50 PDF Wave Practice - Transverse Wave Label and Draw Review/Reinforcement/Practice Activity for students to define parts of a transverse wave and illustrate waves using standard measurements. Great practice activity or test review exercise.
Transverse Waves - L.R. Ingersoll Physics Museum - UW-Madison Transverse Waves A Shive Wave Machine is shown above. A wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time by the transfer of energy without the transfer of matter. When a moving wave consists of oscillations occurring perpendicularly to the direction of energy transfer, it is called a Transverse Wave
Transverse wave - Wikipedia Transverse waves commonly occur in elastic solids due to the shear stress generated; the oscillations in this case are the displacement of the solid particles away from their relaxed position, in directions perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. These displacements correspond to a local shear deformation of the material.



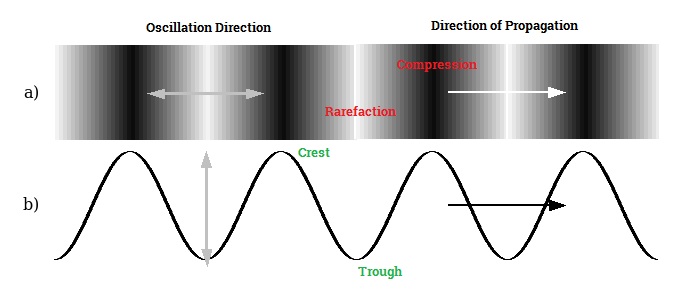
Post a Comment for "38 transverse wave with labels"